Looking for a new CBCT Machine? Get a FREE radiology report on every scan. Learn More.
Buy a CBCT, get radiology reports FREE! Learn More.
Case Studies
Below are a few examples of actual studies our radiologists have reviewed, all of which contained findings outside of the dentition. Drag the arrow across the image to view the specific location of the finding.
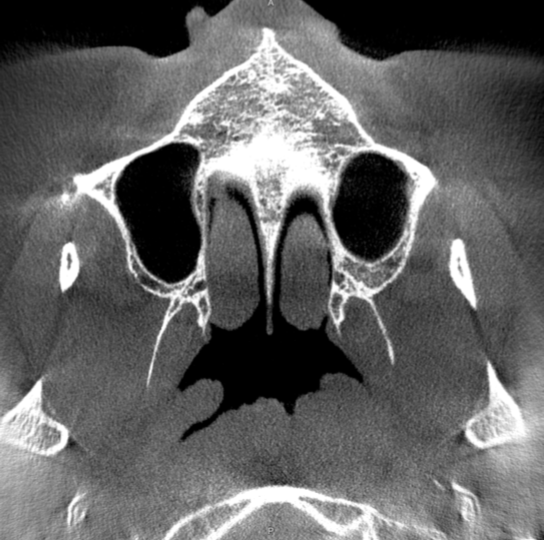
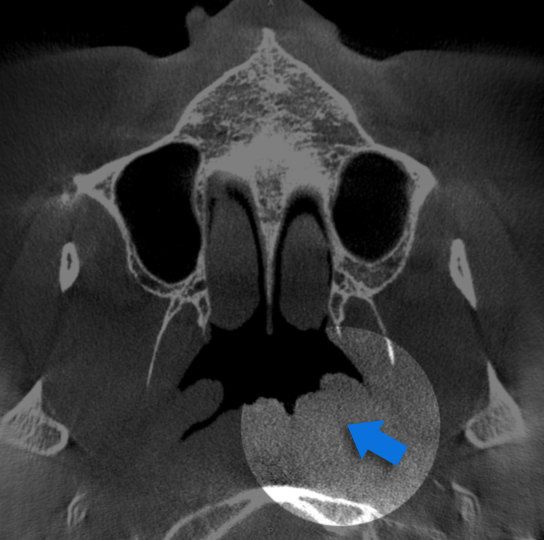
Study 1
Finding: Left Nasopharyngeal Mass.
Abnormal effacement of the left fossa of Rosenmuller, possibly representing a nonvisualized mass lesion. Direct visualization and ENT referral is recommended.
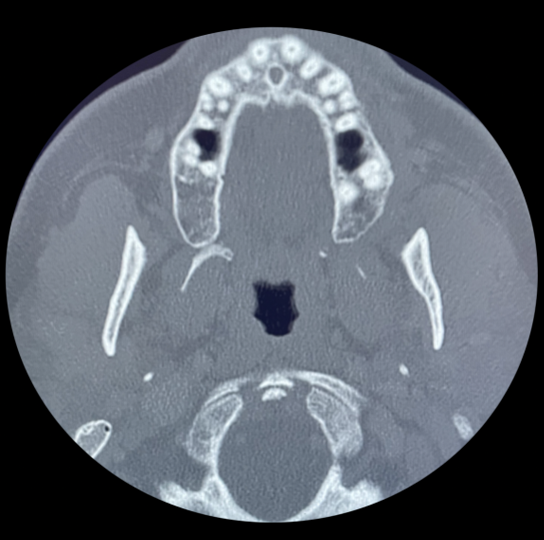
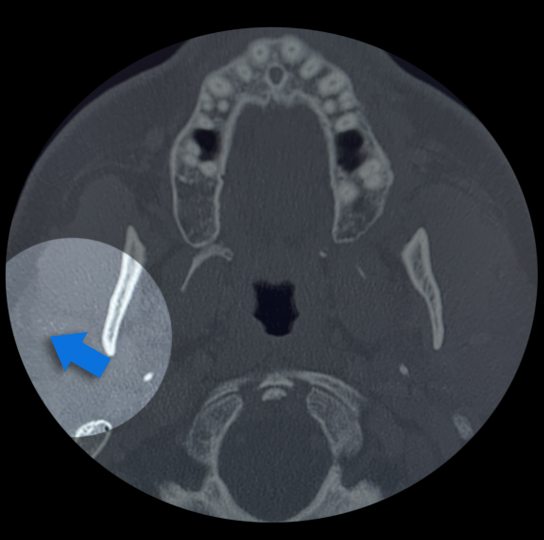
Study 2
Finding: Hypermetabolic mass in right parotid gland.
Suspicious subtle grouped calcifications in the right parotid gland. Using post processing technique to emphasize soft tissue, a subtle mass can be seen in the right parotid gland.
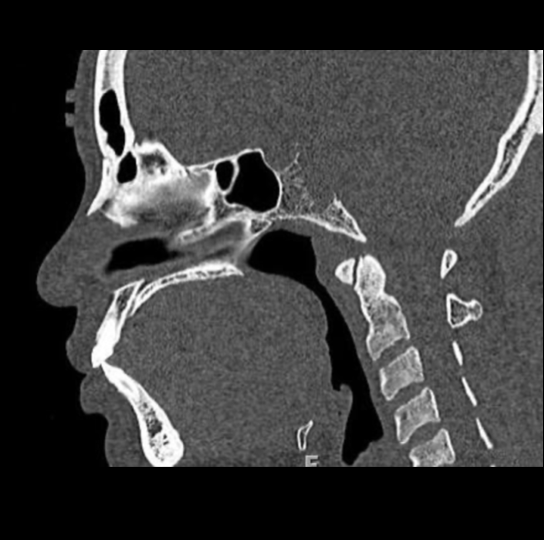
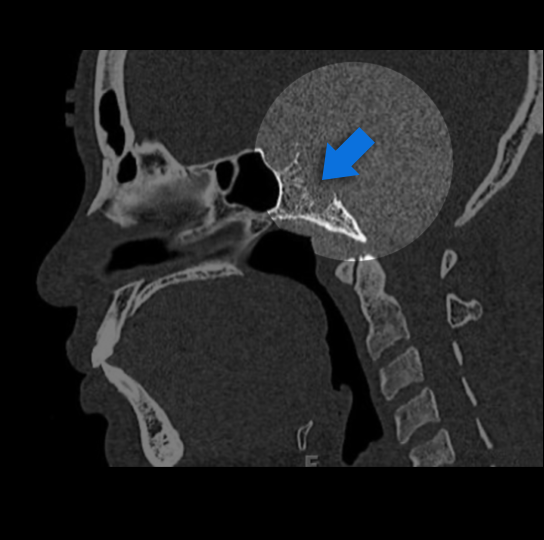
Study 3
Finding: Congestion, airway “fullness”
Soft tissue mass in the right sphenoid sinus, erodes the posterior wall of sinus. Recommend MRI of the skull base to better evaluate.
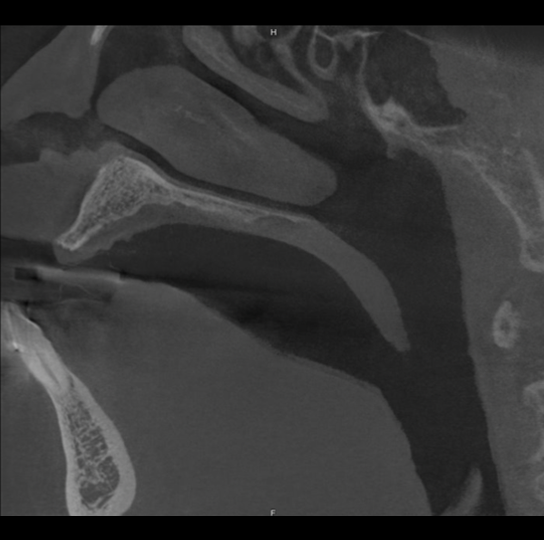
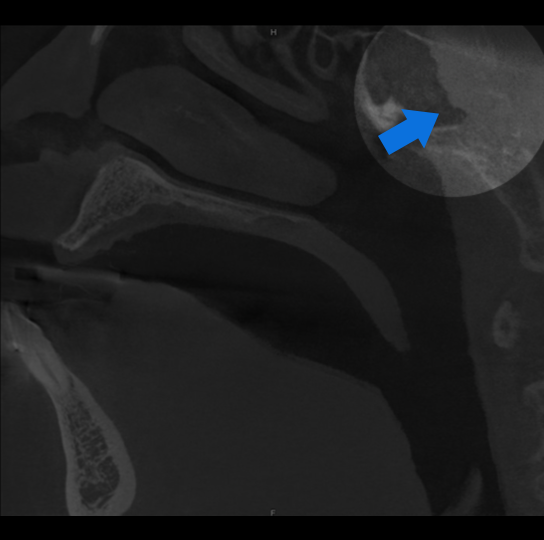
Study 4
Finding: Lytic bone lesion of clivus
Suspicious lytic and erosive bone lesion involving the sphenoid and clivus. Recommend clinical referral and skull base MRI for more definitive evaluation.
MRI follow up found an infiltrating soft tissue tumor, consistent with aggressive chordoma.

Although I feel I'm competent to interpret the scans, I just don't have the time to deeply interpret 80+ scans, other than for the specific tooth pathology I'm evaluating from an endodontic perspective. DentalRay gives me the peace of mind knowing I have a licensed radiologist reviewing the scans from a liability standpoint.
Ryan M. Walsh, D.D.S., M.S.
Advanced Endodontics of Texas
